In tile installation projects, selecting the appropriate hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) is critical to ensuring the construction performance and final bonding effectiveness of tile adhesives. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the key performance parameters of HPMC and offer a HPMC for tile adhesive selection guide tailored to different tile types and construction environments.
I.The role of HPMC in tile adhesives
Viscosity: Directly affects the consistency, sag resistance, and slip resistance of the adhesive mortar. High viscosity provides stronger slip resistance support.
Water Retention: Ensures sufficient moisture for cement hydration during curing, especially on porous substrates or in dry/high-temperature environments, preventing strength loss and hollow voids due to rapid moisture loss.
Modification Degree (Substitution Degree): Affects dissolution rate, resistance to biodegradation, salt resistance, and gel temperature (low-temperature solubility). Higher substitution degrees typically indicate better water resistance and salt resistance.
Dissolution rate: Affects the speed at which the initial viscosity of the adhesive paste is established and the workability during application.
Gelation temperature: Refers to the temperature at which the HPMC solution begins to become turbid and loses its viscosity. HPMC generally has a higher gelation temperature than HEMC (often >65°C). Products with lower gelation temperatures within the HPMC range are more suitable for cold environments.
II.Matching the Optimal HPMC Based on Tile Types
Tile Type | Core Challenges | Optimal HPMC Characteristics | Recommended Solution |
Stone Slabs/Ceramic Tiles (Water Absorption Rate <0.5%) | High slip risk, requiring ultra-high bonding strength | Ultra-high viscosity (>60K or >80K, depending on formulation and other additives), slip-resistant modification | Specialized “large-format” HPMC (e.g., 80K viscosity) |
Stoneware Tiles (Water Absorption Rate 3%-10%) | Balance water retention and workability | Medium-high viscosity (20K–60K, standard range), good water retention | General-purpose HPMC (e.g., 40K-60K) |
Clay Tiles/Interior Wall Tiles (Water Absorption Rate >10%) | Water easily absorbed, high risk of hollow voids | Very High to Ultra-high water retention (>98% is achievable), low to medium viscosity (~20K-40K often preferred) | Specialized “high water retention” HPMC (e.g., 20K-40K viscosity) |
III.Match the optimal HPMC to the construction environment
Environmental factors directly affect the evaporation rate of water in the adhesive mortar, the rate of hydration reaction, and construction operations:
1.High-temperature dry environment (summer/well-ventilated areas)
Challenge: Water evaporates extremely quickly, causing the adhesive mortar to dry out rapidly, significantly shortening the open time and reducing the construction window; cement hydration accelerates but may not be complete due to water deficiency.
Solution: Prioritize water retention! HPMC is generally excellent for this. Select HPMC with the highest water retention performance (water retention value as high as possible, e.g., >98%) and pair it with high-substitution products to enhance temperature resistance. Lower viscosity grades (<40K) can sometimes offer slightly better water retention at equal dosage.
2.Low-temperature, humid environments (winter/bathrooms/pools)
Challenges: Cement hydration slows down at low temperatures, delaying strength development; high humidity or water environments impose extremely high demands on the water resistance and long-term durability of adhesives. A key challenge for HPMC is its relatively high gelation temperature.
Solution: Prioritize gel temperature! Select HPMC with the lowest possible gelation temperature (e.g., <70°C or ideally <65°C if available) to ensure proper dissolution and thickening/water retention functionality at low temperatures (e.g., 5-10°C). Ordinary HPMC (with higher gel temps, e.g., >75°C) may not dissolve completely or experience a significant drop in viscosity at low temperatures. Surface treatment or specific low-gel-temp grades are crucial.
3.Porous substrates (aerated concrete blocks/old mortar layers/untreated cement substrates)
Challenges: The substrate rapidly absorbs moisture from the adhesive mortar, similar to the issue of laying high-water-absorption tiles, leading to moisture loss, insufficient hydration, and reduced bonding strength.
Solution: Dual protection of water retention and penetration!
1.Ultra-high water retention: This is a core requirement. HPMC excels here.
2.Good wetting and penetration: Avoid using products with very high viscosity to ensure the adhesive mortar can effectively wet and penetrate the substrate’s micro-pores, forming mechanical anchoring. A low to medium viscosity (20K-40K) is typically most suitable. Very high viscosity HPMC (>60K) can hinder penetration.
IV. Strategies for Selecting the Optimal HPMC
Define core requirements
Identify the most critical requirements in the current application scenario (anti-slip? Water retention? Low-temperature resistance? Water resistance?), and prioritize core requirements when selecting HPMC types.
Consider synergistic effects
HPMC must synergize well with other additives in the formulation (e.g., Redispersible Polymer Powder, Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer). High-viscosity HPMC may require additional water-reducing agents to ensure workability; HPMC’s excellent water retention creates an optimal environment for cement hydration, enhancing the reinforcing effect of latex powder.
Testing and Validation
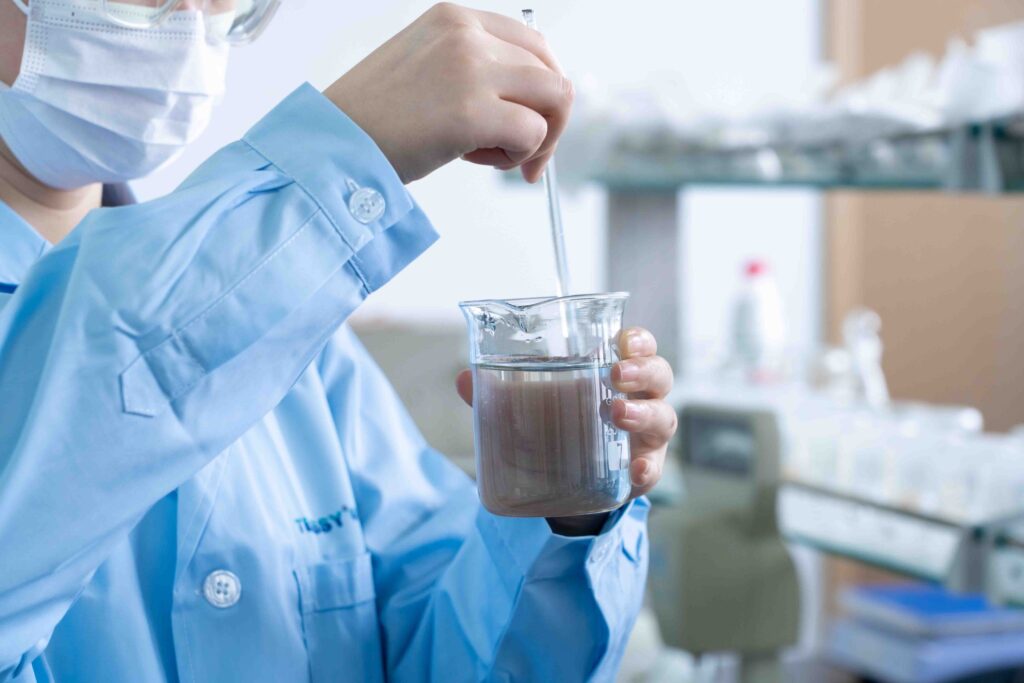

Laboratory pilot tests and on-site construction tests are the final steps to validate the success of HPMC selection. Key Focus Areas:
- Wet mortar state (consistency, sag resistance, slip resistance)
- Open time/adjustment time(Crucial for HPMC in hot/dry conditions)
- Bond strength (original strength, strength after water immersion, strength after thermal aging, strength after freeze-thaw cycles)
- Construction feel (smoothness of application)and Dissolution (especially at lower temps)
Consult the supplier
TENESSY, a professional cellulose ether supplier with extensive industry experience, can recommend the most suitable HPMC grade (considering viscosity, substitution, gel temp, surface treatment) and dosage based on your specific tile type, substrate condition, environmental requirements, and performance objectives.













